Brazil drought – the Readiness Prophylac
The bottom of the ND-GAIN Index when ranked by the water sector
Last month, Sao Paolo’s epic drought made headlines around the world, not simply because that’s strange for a place known colloquially as Terra da Garoa(Land of Drizzle). Ranked by the water sector, Brazil sits at a comfortable 20 in the ND-GAIN index. But officials in that country’s most populous city have worried about water supplies for several years and even wonder if it might cause a riot.
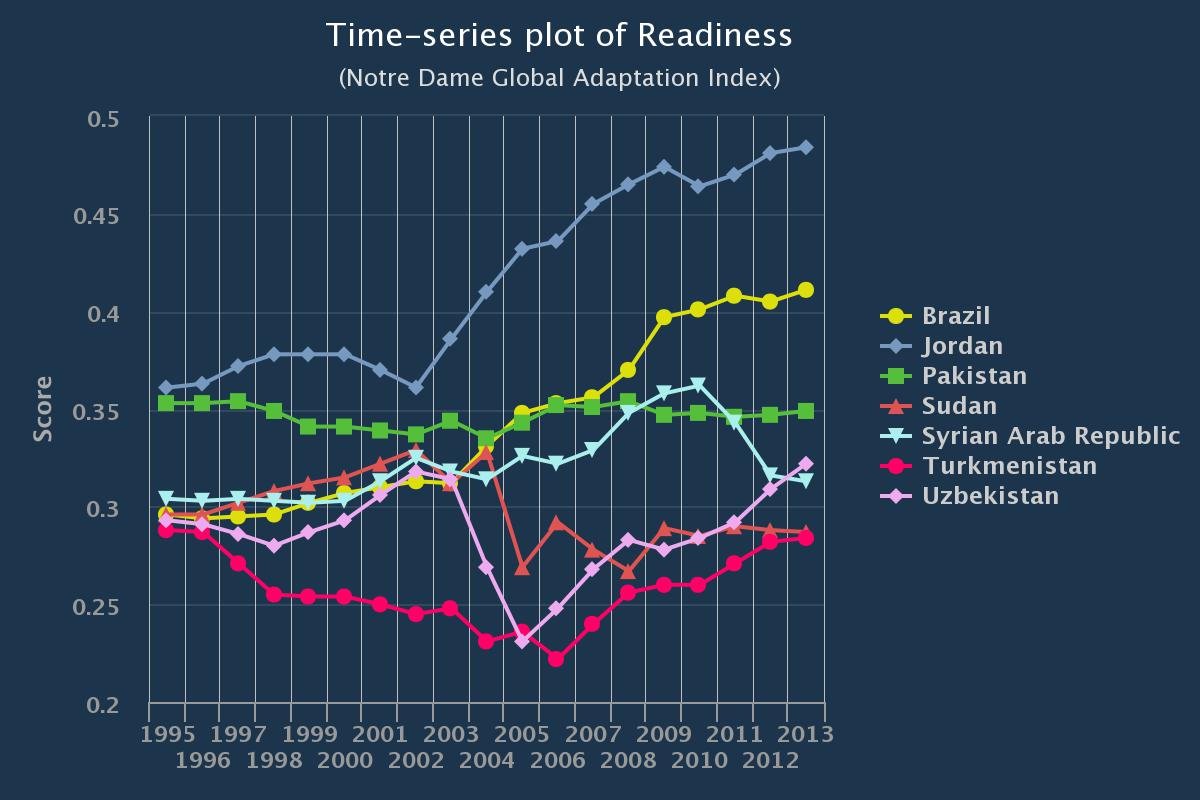
In other parts of the world, of course, drought has been oncoming for decades. These are the kind of places that already have progressed beyond riot stage into all-out-war. Simply consider the bottom of the ND-GAIN Index when sorted for water. That Syria lies at the bottom shouldn’t be surprising.
Other countries – Sudan and Pakistan, for instance – aren’t too surprising either because water shortages have sparked popular discontent. In their cases, droughts in agricultural lands have spurred rural migrations to their cities. Some suggest this contributes to fomenting volatile civil discontent.
I am particularly interested in why those countries that share a low berth on the ND-GAIN rankings seem relatively conflict-free. For instance, comparing the trajectory of Jordan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan to that of Syria, Sudan and Pakistan, the suggestion arises that improving governance, social structure and economic opportunity in countries could prove to be a prophylactic to water-scarcity driven civil conflict.
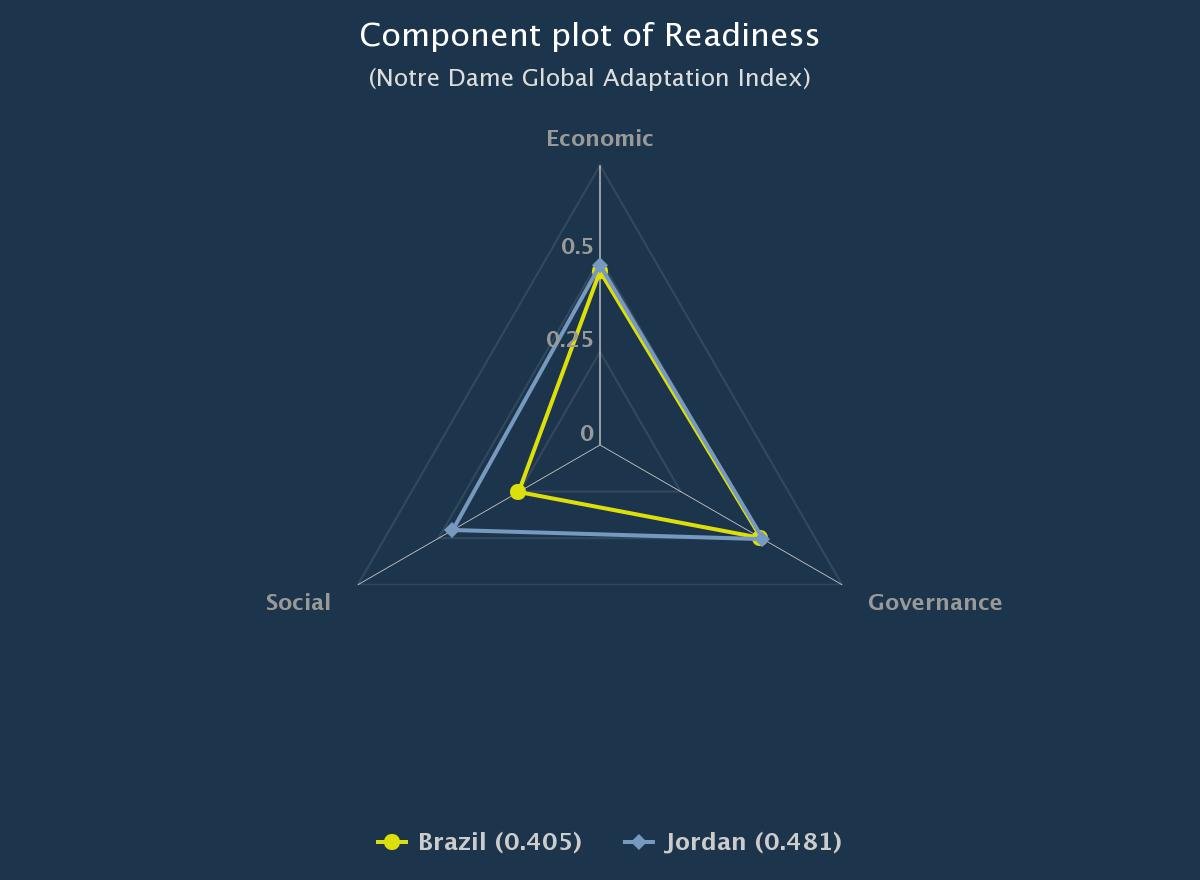
That possibility makes me hopeful for countries such as Brazil, whose readiness also has increased over time. On the graph below, Brazil’s curve resembles a giraffe, just like that of Jordan. So while its readiness rank is 111 in the ND-GAIN Country Index vs. Jordan’s 82, Brazil may be able to increase its resilience to drought and, thus, quell any potential water-scarcity driven unrest. It appears that it might start is in the social sector.
June 12, 2017